3d printing: where are we at with this revolution of the manufacturing industry
Next to industrial and digital revolutions, 3D printing is another technology changing the world. It is an ultramodern manufacturing technique that can be found almost everywhere and not just as tooling in factory settings. By K.A. Gerardino.
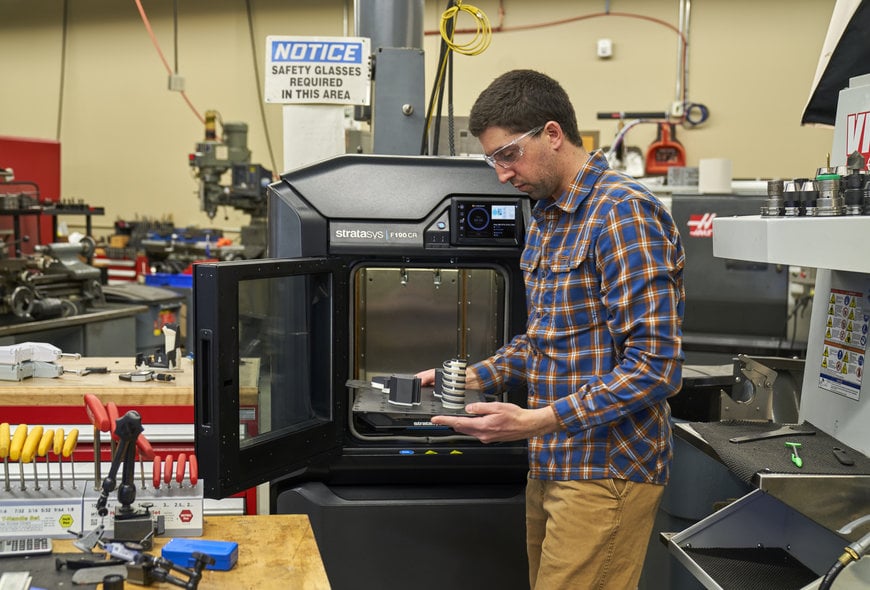

While today’s 3D printing carries some impressive capabilities and is a widespread mode of production used by manufacturers across nearly every industry, it was not always like that. 3D printing has come a long way since additive manufacturing technology was introduced back in the 1980s. To understand this futuristic method, it is helpful to understand the history of 3D printing, what have come before it, and where are we at with this industrial revolution.
How it began
Additive manufacturing started in the 1980s when Chuck Hull invented a process called, stereolithography, now known as 3D printing. He discovered the method, which used UV lasers to create 3D objects layer by layer, after becoming frustrated with the long production times of prototyping. This sparked the next wave of manufacturing practices, and in 1986, he successfully patented his invention, eventually becoming the father of 3D printing. Thus, commercialized availability of additive manufacturing and 3D printing for manufacturers was born.
Endless innovation and development
Since the invention of the first 3D printing rolled into the spotlight, it has been subject to rapid and endless innovation and development. A niche technology, it has opened possibilities for start-ups to present reasonably-priced 3D printers, with major multinational corporations like HP and GE entering the 3D printing space.
3D printing technology has offered various solutions to help tackle the shortcomings that traditional manufacturing methods have for decades. The global 3D printing market is projected to grow from US$18.33 billion in 2022 to US$83.90 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 24.3% in forecast period, 2022-2029, exhibiting a CAGR of 24% during the forecast period, reports Fortune Business Insights.
According to the market research firm, the rapidly increasing digitalization, growing adoption of advanced technologies, such as Industry 4.0, smart factories, robotics, machine learning, and others fuel the demand for online 3D printing for simulation purposes. These technologies increase the chances of broader adoption and greater utilization of this technology across industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare among others.
Significant 3D printing techniques today
We have witnessed the continued evolution of 3D printing in the past year as it transitions from mostly prototyping to widespread use in manufacturing at scale. The great paces made on the technology front mean that today’s printers can provide manufacturers with parts that are faster to develop, more accurate, lower cost, and closer to the point of application. Here are some of the important techniques of 3D printing technology today:
Stereolithography (SLA): Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing process using a vat of liquid UV-curable photopolymer resin and a UV laser to build parts a layer at a time.
Digital Light Processing (DLP): Digital Light Processing displays the image of the 3D model onto the liquid polymer. The exposed liquid polymer hardens and the build plate moves down and the liquid polymer is once more exposed to light. The process is repeated until the 3D model is complete and the vat is drained of liquid, revealing the solidified model.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Selective Laser Sintering is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a high-power laser (for example, a carbon dioxide laser) to fuse small particles of plastics, metal (direct metal laser sintering), ceramic or glass powders into a mass that has a desired 3-dimensional shape.
Inkjet Binder Jet: A binder jetting machine will distribute a layer of powder onto a build platform. A liquid bonding agent is applied through inkjet print heads bonding the particles together. The build platform will be lowered and the next layer of powder will be laid out on top. By repeating the process of laying out powder and bonding, the parts are built up in the powder bed.
Selective Deposition Lamination (SDL): SLD is a 3D printing process using paper. The process involves layers of adhesive coated paper (or plastics or metal laminates) that are successively glued together with a heated roller and cut to shape with a laser cutter layer by layer. A roller with the material moves each new sheet of material over the last and repeats the process until the object is completed.
Electronic Beam Melting (EBM): EBM is like laser melting, but working with an electron beam instead of a laser. The machine distributes a layer of metal powder onto a build platform, which is melted by the electron beam. The build platform is then lowered and the next layer of metal powder will be coated on top. The process of coating powder and melting where needed is repeated and the parts are built up layer by layer in the powder bed.
Fused Filament Fusion (FFF): FFF is an additive manufacturing technology, it is now the most popular 3D printing process, and in FFF a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material is used. Through a moving, heated printer extruder head, molten material is forced out of the print head’s nozzle and is deposited on the work piece layer by layer to form the desired Product.
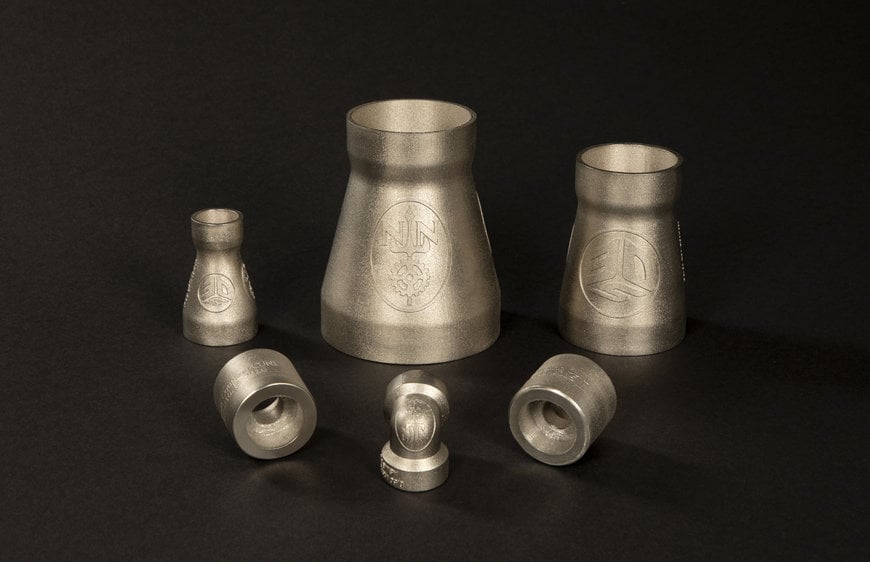

Various pipe fittings printed by Newport News Shipbuilding using Certified CuNi30 material on 3D Systems’ Direct Metal Printing hardware. Source: 3D Systems
Innovative 3D printing company to date
Every manufacturing company knows that having a vision before you have even started the process of prototyping is where the treasure lay. When great concepts are combined with technology, the possibilities can take form. Some companies have succeeded connecting the competences of 3D printing to solve the 21st century’s most perilous issues. IMARC Group released its top 3D printing companies in the world:
Stratasys Ltd is one of the top companies that are at the forefront of 3D printing technology. It caters to various end-use industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical start-up, as well as tech giants. It also provides decades of knowledge, consulting, training, workflow management, and end-to-end support.
3D Systems, Inc. has been leading the additive manufacturing innovation since its inception. Its portfolio includes hardware, software, and material solutions that span from plastics to metals, and is backed by industry-specific engineering expertise housed in the application innovation group. It also offers a combination of solutions, expertise, and innovation that helps users defy conventional manufacturing limitations and maximize the value of additive manufacturing.
Materialise NV has combined the largest group of software developers in the industry with one of the largest 3D printing facilities in the world to enable new users for the extraordinary potential that 3D printing offers. The company has created a range of software solutions and 3D printing services to form the backbone of the 3D printing industry.
EOS is a worldwide provider for industrial 3D printing of metals and plastics. The company brings responsible manufacturing solutions via industrial 3D printing technology to manufacturers across the globe. Today, the company’s industrial 3D printing systems make it possible to respond quickly to the demands of volatile markets and address trends like the increasing customization of end products.
ExOne has been the global leader in industrial 3D printing systems company in the United States for more than 20 years. It uses Binder Jetting technology, an additive manufacturing process, to selectively join a binding agent with industrial-grade powder particles. It also created a custom finished product from a 3D CAD file using metal, sand, or ceramic materials.
Voxeljet AS is a global innovator and technology driver for advanced 3D printing systems and solutions in production environments. The company is equipped with state-of-the-art binder jet components and seamlessly integrated into partially or fully automated production systems. It is also sustainably shifting the economic parameters and possible applications of additive manufacturing in the industry.
Hewlett Packard (HP) Enterprise Company aims to create technology that makes life better for everyone, everywhere across the globe. HP Personalization has partnered with 3D printing to make any idea, large or small, simple, or complex, a reality. Furthermore, HP MJF 3D printing technology can unlock new possibilities that complement CNC, injection moulding, as well as additive manufacturing, and powder-based technologies.
SLM Solutions Group is one of the leading providers of industrial metal 3D printing machines focused on metal additive manufacturing and multi-laser technology. They find applications across end-use industries including, aerospace and defense, automotive, energy, healthcare, tooling, and research.
EnvisionTEC offers a wide variety of 3D printing systems with the ability to mass-produce polymer parts. ETEC printers deliver parts with exceptional accuracy, superior part properties, fine feature detail, and a smooth surface finish. They also provide scale and cost that are competitive with traditional manufacturing techniques like injection moulding.
CleanGreen3D is an Irish company that bought the assets and IP of the former Mcor Technologies Limited, an innovative manufacturer of the world’s most affordable, full-colour, and eco-friendly 3D printers. It makes use of ordinary business letters and A4 papers as build material. Its vision is to make 3D printing more accessible to everyone by rendering durable, stable, and tactile models.
Optomec, Inc. offers production equipment and digital solutions such as 3D printed metal, 3D printed electronics, for the digital age. It aims to reduce lifecycle costs for long-term asset management. The company also enables customers to not only print full 3D parts but also add materials onto existing 3D parts that were produced using conventional manufacturing methods.
Groupe Gorge specializes in high technology and is imbued with a strong entrepreneurial culture. It is one of the leading players in its high-tech markets and operates around the world in innovative and growth sectors such as drones, robotics, engineering, and protection systems. Moreover, the company is enabling major players to find routes to successful production processes by providing 3D printers and new premium materials.
Ultimaker is the market leader in desktop 3D printing that has built an open and easy-to-use solution of 3D printers, software, and materials. It is increasing business flexibility and continuity by 3D printing parts with software trusted by over 800,000 users. Their easy-to-use FFF desktop 3D printers can save time and money while streamlining the workflow and delivering the quality results that are expected.
Renishaw plc is a systems manufacturer and solutions provider for additive manufacturing or 3D printing. It is one of the leading manufacturers of advanced metal additive manufacturing systems and an expert provider of customer-tailored solutions. The company makes use of thin layers of materials to create complex shapes, which cannot be produced by ‘traditional’ techniques such as casting, forging, and machining.
Beijing Tiertime Technology Corp. Ltd strives to deliver additive manufacturing solutions to a wide variety of fields, such as science, mechanical engineering, industrial design, low-volume manufacturing, and education. The company is China’s first 3D printer manufacturer that launched the nation’s entry into the additive manufacturing age with the Inspire industrial line.
XYZprinting, Inc. is one of the leading global providers of comprehensive 3D printing solutions. The company offers desktop 3D printing products and services and is venturing into the industrial additive manufacturing arena. Moreover, XYZprinting is backed by the world’s leading electronic manufacturing conglomerate, New Kinpo Group, which earns more than US$36 billion in revenues annually and has more than 8,500 engineers in research and development across four continents.
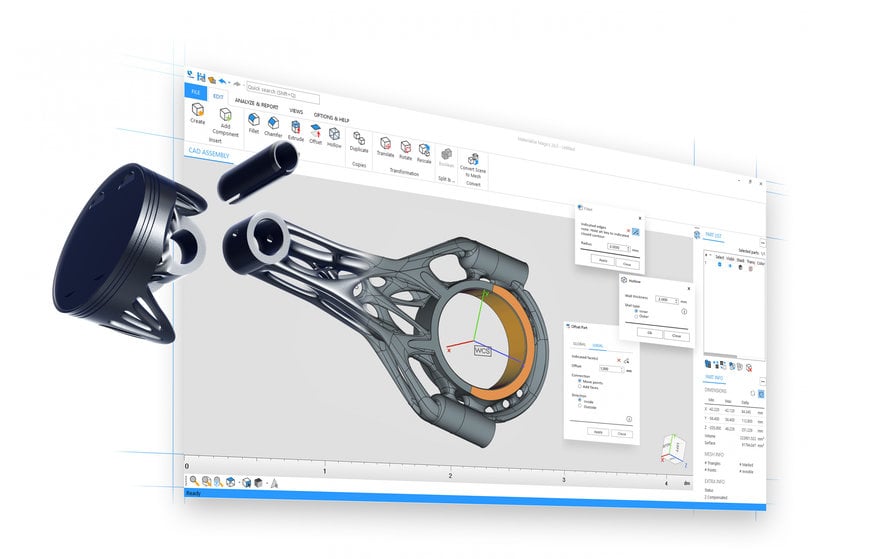
Materialise Magics 26 with CAD and mesh capabilities for 3D printing. Source: Materialise
3D printing trends in 2023
With favourable balance sheets and a multitude of latest offerings, 3D printing industry is expected to accelerate adoption in manufacturing processes and make meaningful advances in 2023 and beyond.
These are a few trends that are expected to dominate this year:
Lower cost of 3D printing: One of the major trends in the 3D printing industry is the decreasing cost of 3D printing technology. As 3D printing becomes more accessible, prices are decreasing and the technology is becoming more affordable. This will make it easier for businesses and individuals to utilize 3D printing technology and will offer a new world of options.
Improved speed and quality: Speed and quality are two of the most important aspects of 3D printing. It is becoming faster and more accurate with new advancements coming in. This will enable businesses to create better products more quickly and efficiently and will lead to a greater level of customization for consumers.
Increased use of materials: In the past, 3D printing was limited to plastics and metals. However, as 3D printing technology continues to evolve, an increased use of materials, such as ceramics, polymers, and even food items are likely to happen in the future. This will open a new world of possibilities for 3D printing and will allow businesses to create products that were not previously possible.
The development of multi-material 3D printing allows to produce objects with multiple materials and properties. This technology has the potential to greatly expand the range of applications for 3D printing, including the production of functional prototypes, customized medical devices, and even consumer products.
There has also been a trend towards the development of more advanced 3D printing technologies, for instance: 4D printing and 5D printing. 4D printing involves the use of materials that are capable of changing shape or properties over time in response to external stimuli, such as heat or moisture. 5D printing, on the other hand, involves the use of multiple 3D printing techniques to create objects with complex structures and functions. These technologies have the potential to significantly expand the capabilities of 3D printing and could lead to the development of new and innovative products.
Widespread adoption: As 3D printing becomes more affordable and accessible, it is expected to be adopted by a larger portion of the population. This will open new prospects for individuals and companies to utilize 3D printing technology, as well as lead to new innovations in the industry.
A reduction in carbon emissions is to be expected, as parts now require less transportation. Parts can now also be produced more sustainably as it is easier to customise the materials and dimensions of a part, leading to waste reduction. On that note, its on-demand production capabilities will also ensure that one can only manufacture parts that they need when they need them, resulting in minimal parts wastage and excess.
Shift from process automation to workflow automation: The promise of large-scale industrial 3D printing requires us to automate not only each individual process but also the flow between them. This is what we call workflow automation.
Fred Vancrae, CEO of Materialise, explained, “We see the same requirement in a medical industry where workflow automation is needed to address the dramatic increase of customized 3D printed solutions. The good news is that the ability to meet this need is growing thanks to the creation of software platforms that allow manufacturers to define their own unique 3D printing process. Several companies including Materialise now offer these solutions to customers allowing them to automate not just the individual 3D printing processes but the entire 3D printing workflow from order intake to delivery and everything in between.”
Smart distributed manufacturing: Smart distributed manufacturing that is enabled by 3D printing when done in a strategic way can be a successful recipe, rather than an ad hoc response to problems with global supply chains, Fred Vancrae emphasized. “3D printing enables design optimizations that provide weight performance, time saving and supply chain benefits that are impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. In many cases, these benefits create cost advantages that impact the overall end-to-end manufacturing costs from design to delivery. In fact, the ability to reduce the overall manufacturing costs is cited as the most important benefit of 3D printing but that does not necessarily mean that the 3D printing process itself is cost efficient. Increasing material and energy prices have only driven up the costs even more,” he stressed.
“There are several factors that determine the cost of 3D printing parts. This comprises of the materials required, production time per part, and the type of printer. However, there are two important ways to reduce this,” Fred pointed. “The first step is by working more efficiently to increase production capacity. Software plays a major role in this by making it possible to optimize the build. We can also tune the printing process to make it more efficient and repeatable,” he indicated.
“The second step is using tools and improve quality; but quality comes at a cost. Looking at certified manufacturing in the medical or aeronautics industry for example, we see that up to 70 percent of the production cost is in quality control. 3D printing continues to transform the factory floor, as companies increasingly turn to the technology for large-scale production. But to accelerate this adoption, the industry will have to make extra efforts to reduce the cost of 3D printing,” Fred added.
Data security and data integrity: Data security is important in any form of manufacturing whether traditional or smart in both cases as addressed by Fred Vancrae in his video about the biggest 3D printing trends for 2023.
“Companies share their unique designs with contractors and suppliers and they want to know that their design data remain secure. With 3D printing, manufacturers may want to plan and scale up the production of their 3D printed parts into thousands or even millions. They need to optimize and fine-tune their unique printing process to make it efficient, reliable, and repeatable across multiple production sites. A smart production process ensures that all 3D printed components have the same quality no matter where they are produced. Creating such a process is complex and time consuming but it allows companies to leap ahead of the competition. That is why in addition to data security and data integrity, the close and secure link between the design on one hand and the production parameters on the other hand is becoming top of mind for companies that embrace digital manufacturing,” he revealed.

Additive Minds Academy: blended learning formats
Conclusion
The adoption of 3D printing technology reaches new heights each year. Over the last thirty plus years, it has become an integral part of the manufacturing industry. The future is bright for 3D printing technology in 2023, as it will help companies scale up their operations into volume production and advance their overall utilization.

